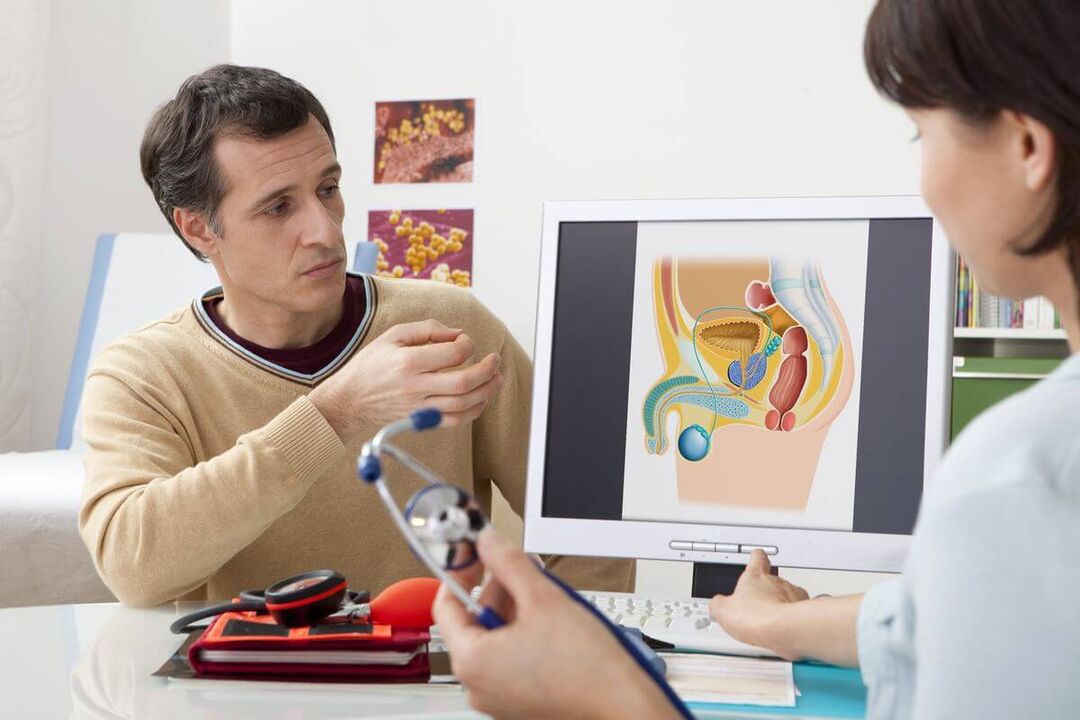
Prostatitis is the most common disease of the male genitourinary region. Prostate inflammation is the result of a man's indifference to his health. Prostatitis can be inconvenient and can lead to serious complications.
cause of disease
The prostate produces a secret responsible for the motility of sperm, normalization of the pH of the urinary tract, and protection of the urogenital system from infection.
Prostatitis most commonly affects men between the ages of 25 and 50. Pathology occurs when infectious agents enter prostate tissue from genitourinary organs. Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus, and Escherichia coli can be used as infectious agents. Inflammation occurs based on the following predisposing factors:
- low temperature;
- A sedentary lifestyle, occupations that force a person to be in a sitting position for long periods of time - driver, office worker;
- metastatic urological diseases;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- Violation of normal sexual intensity - excessive activity is as harmful as frequent partner switching and prolonged abstinence;
- Violation of body defenses - chronic stress, insomnia, malnutrition, excessive physical activity;
- decrease in immunity;
- Inadequate personal hygiene.
Chronic poisoning such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or taking drugs can also increase the risk of prostatitis.
symptoms of disease
Prostatitis can occur in acute or chronic forms. Symptoms of acute prostatitis include:
- pain in the lower back and groin area of varying intensity;
- difficulty urinating;
- a burning sensation when trying to urinate;
- Violation of erectile function - premature ejaculation, reduced severity of orgasm, weak erection;
- fever, chills, fever;
- Psycho-emotional state disorder - depression, increased anxiety, decreased self-esteem.
Without proper treatment, acute prostatitis may become chronic with periodic exacerbations and remissions. Patients experience pain of varying intensity and may have problems with sex - pain during and after sex, decreased erections, feelings of helplessness and disappointment.
During the inflammatory process, the foci of infection spread to other organs in the male urogenital area. The most common complications of prostatitis include:
- Seminal vesiculitis - inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- Posterior urethritis - inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- Prostatic abscess - a serious bacterial disease;
- Cysts and stones of the prostate;
- Ejaculation disorders;
- Infertility caused by a violation of the synthesis of prostatic secretions.
Complications of prostatitis are often the result of self-medication. Uncontrolled intake of antibiotics and other drugs can adversely affect the gut flora, reduce immunity, but have no desired effect on the condition of the prostate.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The disease is characterized by specific clinical manifestations, so diagnosis is usually not difficult. In addition to the analysis of patient complaints, the following data were considered:
- Rectal and prostate examination;
- General and biochemical analysis of urine;
- collection of glandular secretions;
- Prostate ultrasound;
- Spermogram - to determine the risk of infertility;
- CT or MRI - to rule out the presence of benign or malignant tumors.
In the treatment of prostatitis, a comprehensive approach is used, including conservative therapy, the use of physical therapy, and dietary and lifestyle changes. The dominant role in treatment is drug therapy.
The main task of conservative treatment is to eliminate the inflammatory process. For this, antibiotics are prescribed. The choice of drug depends on the type of bacteria causing the pathological process. Antimicrobials are offered in 4-6 week courses.
To normalize urination, alpha1-blockers were prescribed. The preparations of this group help to relax the glandular muscles, relieve pain and relieve swelling.
The list of drugs used to exacerbate prostatitis includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Antidepressants are necessary to normalize the patient's psycho-emotional state and eliminate increased anxiety and depressive symptoms.
massage
Prostate massage is one of the most effective physiotherapy methods for treating pathology. Finger massage is performed rectally and affects prostate tissue. During the massage, the patient should lie on their side. Massage consists of stroking and pressing movements with the index finger. Prostate massage is performed with a full bladder.
Physiotherapy
Other treatments include the following physical therapy:
- Laser therapy is a treatment method based on the use of light beams for therapeutic purposes;
- Acupuncture - injecting drugs into biologically active parts of the body;
- microwave hyperthermia - a treatment method based on the use of electromagnetic wave energy;
- Ultrasonic shock;
- Medicinal microenema - If physical therapy procedures are not possible, the introduction of a drug solution into the rectum is prescribed.
Surgery is required as complications develop, such as a seminal vesicle abscess or suppuration.
During treatment, patients are advised to make lifestyle changes: follow the principles of a healthy diet, normalize sleep, and ensure moderate physical activity.
prevention
Preventive measures to prevent prostatitis from getting worse include:
- observe personal hygiene rules;
- Normalization of sex life, exclusion of casual sex;
- exclude bad habits - smoking, drinking and drug use;
- Make sure your bladder is emptied regularly;
- using plenty of fluids - helps with more frequent urination, filtering out infectious agents from the prostate;
- use foods high in protein and vitamins;
- Alternate sedentary work with moderate physical activity;
- timely detection and treatment of infectious diseases;
- reduce daily stress levels;
- Boost immunity.
The appearance of the first signs of inflammation should always be the basis for contacting a doctor. First, it is important to identify and treat urinary and STDs. Prostatitis can only be treated in a medical facility. Self-treatment at home can be dangerous and lead to complications.